Mapping consumer-led frauds in digital lending
Digital lending fraud is rising rapidly. This blog maps fraud risks across lending stages and explores how lenders can balance trust, innovation, and risk mitigation.
India suffered cyber fraud losses amounting to Rs 11,333 crore in the first nine months of 20241. RBI’s annual report further underscores the escalating issue, revealing that bank fraud cases in India have surged by 166% to over 36,000, while online fraud cases have grown by an alarming 334% year-on-year to 29,082 in FY242.
Several factors contribute to this troubling trend:
Faster account openings: Quick onboarding processes aimed at better UX create exploitable gaps for fraudsters.
Advanced fraud techniques: Fraudsters use sophisticated tools for data breaches and credit card theft.
Low cybersecurity awareness: Poor understanding of secure banking practices leads to phishing and OTP scams.
When we think about fraud in digital lending, the spotlight often shines on stories of illegal loan apps (think Chinese loan apps!), scamsters preying on unsuspecting customers, and the challenges of digital literacy in navigating financial platforms. And rightfully so… these issues dominate headlines, spark regulatory interventions, and paint a relevant picture of the risks that come with the rapid digitization of finance.
But trust in digital lending is a two-way street. While financial institutions work hard to gain the trust of their customers3, they, too, must place immense trust in the authenticity and intent of the borrowers they serve. For lenders, this trust isn’t just an act of goodwill… It's a business imperative.
The burden of managing this trust asymmetry often falls squarely on the shoulders of lenders, who must not only protect their books from bad actors but also ensure that fraud prevention measures do not alienate genuine customers. It's a tightrope walk, one that requires innovation, vigilance, and a deep understanding of how fraud evolves across the digital lending journey!
This blog flips the narrative to explore fraud from the lender’s perspective, mapping risks across the digital lending journey and highlighting the tools and strategies that sustain trust in this ecosystem.
Stages of the Digital Lending Journey
The digital lending journey unfolds in three critical stages:
Onboarding and KYC: This is where borrowers enter the system, providing personal and financial details. Verification processes like eKYC ensure identity authenticity and eligibility.
Underwriting and Decisioning: At this stage, lenders assess creditworthiness by analyzing data, including credit history and income, to make informed loan approval decisions.
Disbursal and Collections: Once approved, loans are disbursed instantly, with lenders managing repayments and addressing delinquencies through structured collection processes.
Each stage is an exercise in balancing user experience for borrowers with risk mitigation for lenders, considering the competitive nature of this sector.
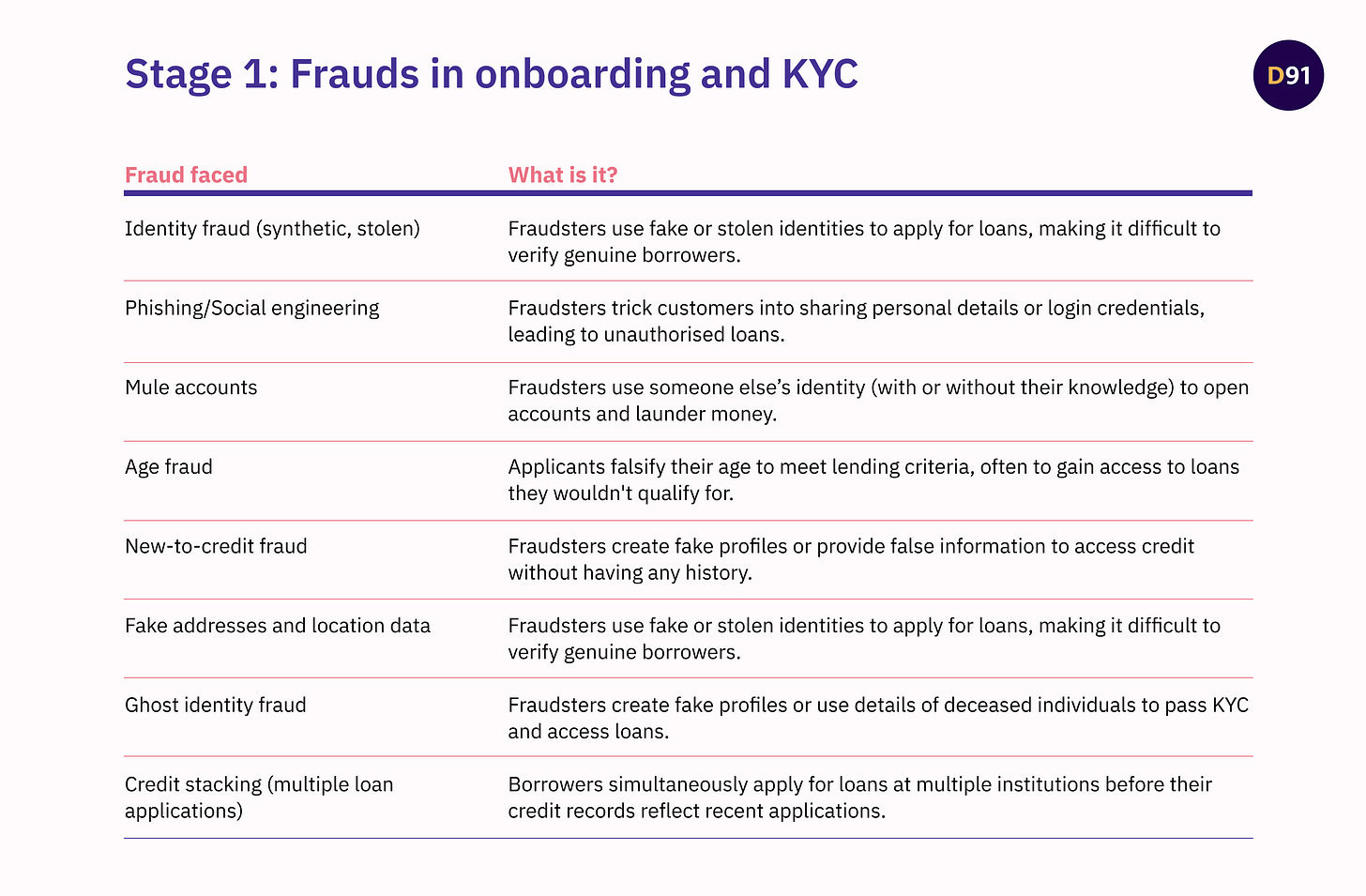
Stage 1: Frauds in Onboarding and KYC
Fraud during the Onboarding and KYC phase arises because it is the gateway to the digital lending ecosystem, where lenders are particularly vulnerable due to several factors. Here’s how the loan journey looks like at this stage:
The reliance on borrower-provided information creates opportunities for fraudsters to submit falsified data, while the push for fast approvals often compromises thorough verification4. Scaling challenges, such as managing high application volumes, can strain resources and create gaps in detection systems. Here’s what frauds during onboarding and KYC look like.
How does this impact digital lending outcomes?
Frauds in onboarding and KYC increase verification costs, delay loan approvals, and strain resources into verifying authenticity, forcing lenders to adopt stricter criteria that may exclude deserving borrowers. Regulatory risks and reputational damage further complicate operations. For borrowers, fraud prevention measures can mean longer wait times, stricter scrutiny, or even unjust rejections, eroding trust in digital lending platforms.
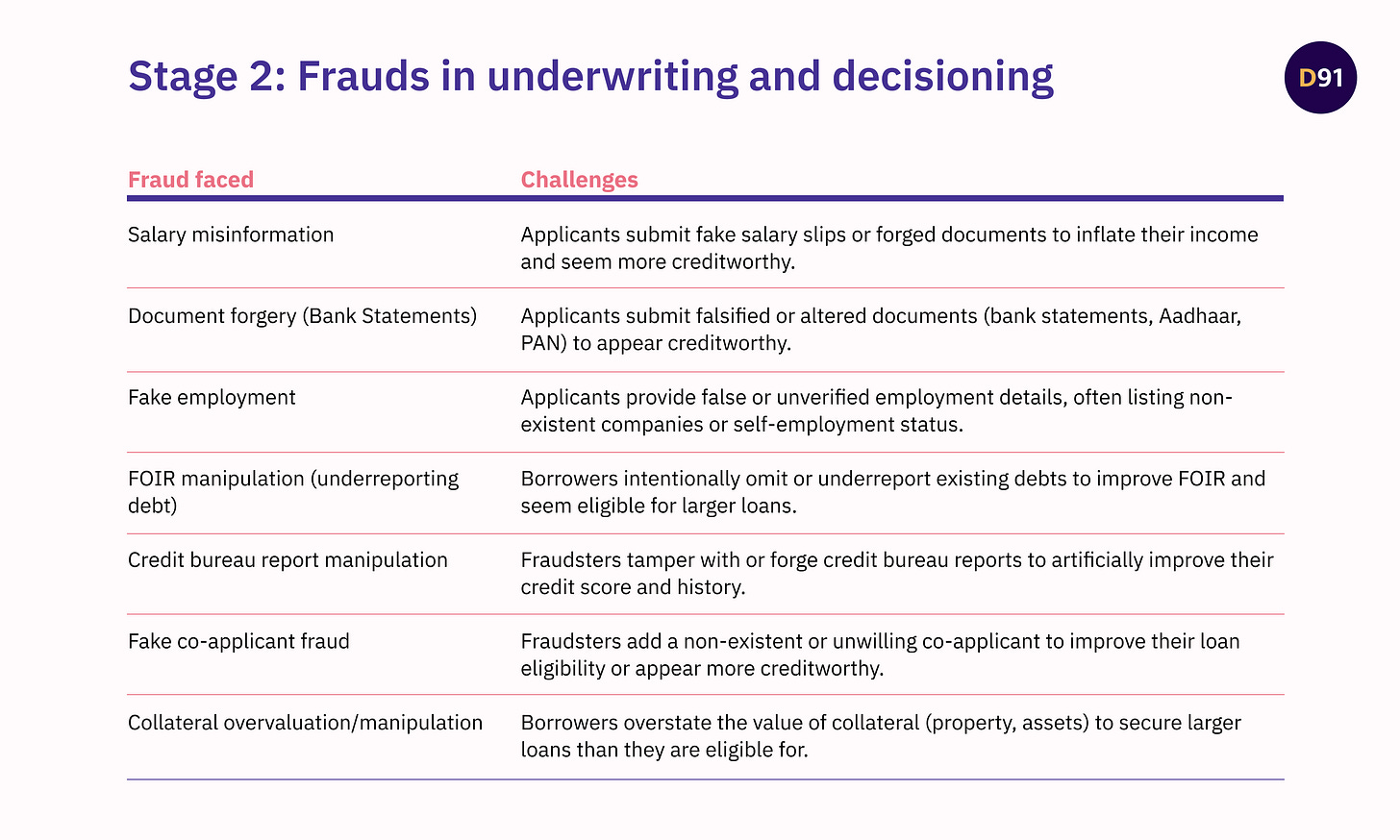
Stage 2: Frauds in Underwriting and Decisioning
The underwriting and decisioning stage is where lenders assess a borrower’s creditworthiness and decide whether to approve a loan. A typical application undergoes the following checks.
This phase is particularly vulnerable to fraud because it relies on accurate financial and credit data, much of which is provided by the borrower. Fraudsters exploit this dependence by submitting forged documents, inflating income, or hiding existing debts to manipulate risk assessments in their favour. This stage represents a high-stakes balancing act for lenders and is most directly linked to potential rise in NPAs
How does this impact digital lending outcomes?
Frauds at the underwriting stage compromise the accuracy of risk assessments, leading to bad loans and increased non-performing assets (NPAs). Additional verification costs strain operational budgets, while repeated fraud undermines the effectiveness of credit scoring models. This creates challenges in scaling operations and maintaining portfolio quality. For borrowers, enhanced fraud detection measures may slow loan approvals and impose stricter eligibility criteria, potentially excluding deserving applicants. This can erode trust in lending platforms, particularly for first-time borrowers.
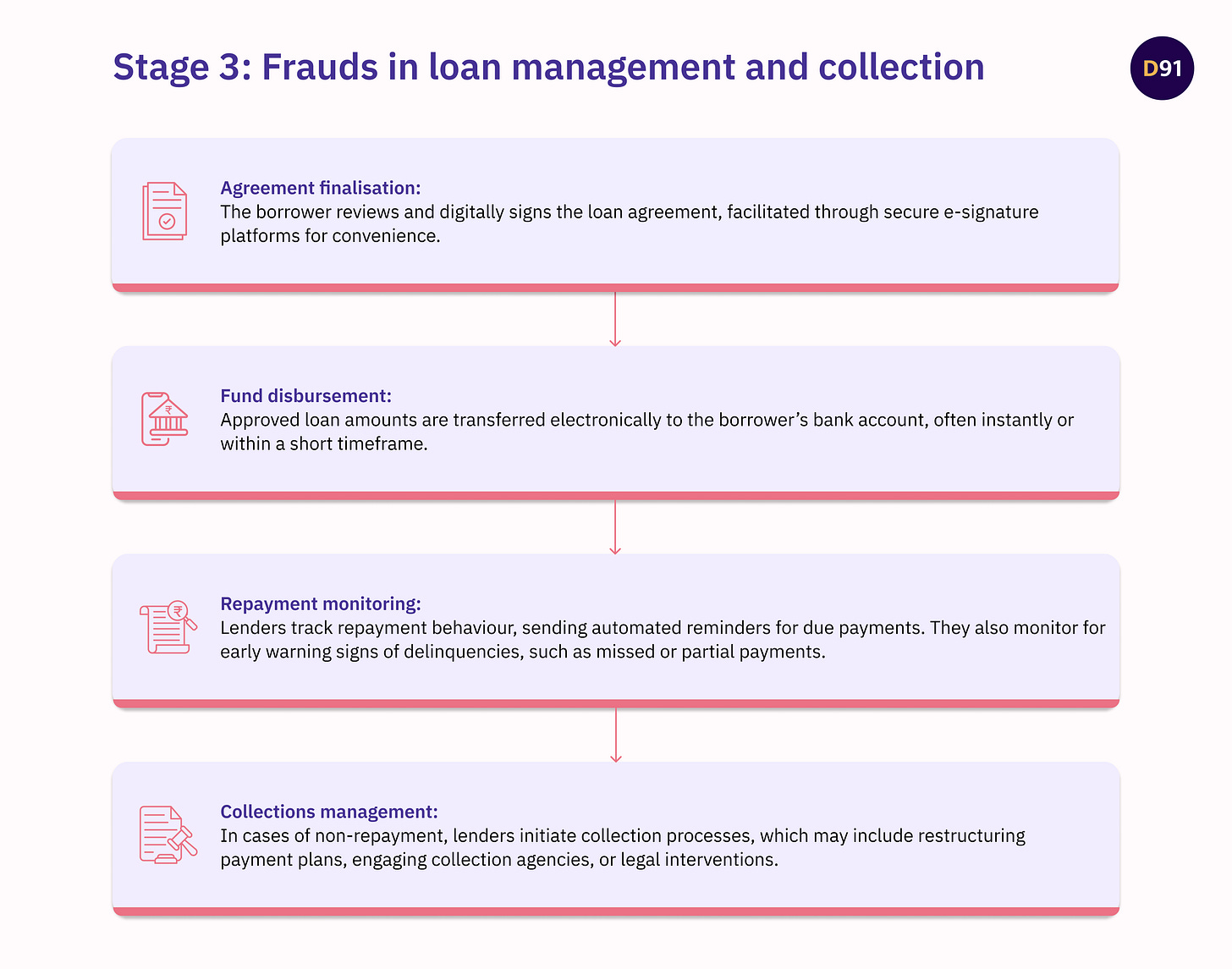
Stage 3: Frauds in Loan Management and Collection
The loan management and collection stage involves monitoring repayment behaviour and ensuring timely recovery of loans. Once the loan is approved, it undergoes the following stages.
Lenders are vulnerable at this stage due to the decentralized nature of repayment (multiple points and methods of payments available) and the challenges of tracking borrower behaviour post-disbursement. Fraudsters exploit these vulnerabilities by using tactics like account takeovers, false insolvency claims, and misrepresenting collateral to evade repayment obligations. Additionally, fraudsters may manipulate repayment records or provide false contact information to avoid traceability during collection efforts. For lenders, the inability to recover loans not only impacts financial stability but also increases operational costs and legal risks.
How does this impact digital lending outcomes?
For Lenders, frauds during loan management increase delinquencies and recovery costs, reducing overall profitability. Complex fraud schemes, such as loan cycling and collection evasion, require significant resources to address, adding operational strain. Fraud prevention strategies, such as stricter monitoring and enforcement, can inadvertently pressure genuine borrowers, particularly those facing legitimate financial difficulties.
Conclusion: Building Resilient Fraud Mitigation Strategies
Mapping frauds across the digital lending journey highlights the intricate challenges lenders face in safeguarding their operations while maintaining a seamless borrower experience. For lenders, understanding these fraud mechanisms is only the first step. Addressing them requires a proactive approach, combining advanced technologies, collaborative frameworks, and stringent regulatory adherence. In the second part of this blog series, we will delve deeper into the tools and strategies lenders employ to detect, prevent, and mitigate these fraud risks.
https://thewire.in/tech/india-lost-rs-11333-crore-to-cyber-fraud-in-2024/?ref=thisweekinfintech.com
https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/AnnualReportPublications.aspx?year=2024
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/technology/banks-increase-employee-background-checks-as-mule-accounts-and-frauds-rise/articleshow/115873844.cms
https://www.bureau.id/blog/balancing-fraud-prevention-vs-user-experience-in-a-digital-world
All artworks are designed by Smriti Krishna.
If you enjoyed reading this blog and would like to receive more such articles from D91 Labs, please subscribe to our blogs here.
To read more about our work, visit our website
You can follow us on Twitter | LinkedIn | Instagram | WhatsApp