Can digital payments increase the access to capital for a small business?
Using proprietor data from the Indifi - a lending fintech, this research paper highlights the positive relationship between digital payments and fintech lending in India.
Not very long ago, the image of a small kirana shop owner clutching a worn-out leather wallet with a bunch of crumpled banknotes, was a familiar sight. Today, for a lot of small business owners that image has been replaced by digital payments made via smartphones - may it be in the city, suburbs or far-off villages. Now, digital payments have dual roles - it has replaced cash for many of us and it also serves as a record of our payment history, buying habits, our aspirational purchases, and financial discipline.
But here’s what is interesting about small businesses adopting digital payments. In the past obtaining a loan for a small business often required cumbersome process such as submitting thick files of financial statements, invoices, tax receipts, and shop licenses and in many cases the loan was offered against the business as collateral. But today, with the adoption of digital banking this process has transformed.
Have you heard of this paper where the researchers1 from IIM, HBS and Wharton have rigorously studied the relationship between digital payments (a.k.a cashless payments2 as termed in the paper) and the ability to access affordable credit from a fintech? Here’s the key finding of the paper -
The higher usage of digital payments by businesses is strongly associated with better borrowing outcomes. This means that these businesses have a higher chance of getting their loans approved with lower interest rates and larger loan amounts from fintech lenders!
For many businesses, these digital payment records are viewed as a form of “digital collateral” that opens their access to capital.
The Indian case study
This study is based on data provided by Indifi, an online lending platform that grants unsecured loans to micro and small businesses, such as taxi drivers and corner stores, in India. The data includes 3,00,000 unsecured loan applications from 2015 to 2022 as well as the whole information set gathered by the FinTech lender to screen applications, the financing outcomes and the loan performance as of 2022. This includes information on industry, location, the number of years of operations of the business, and the age of the business owner. For applicants who possess a credit history, the dataset also includes the associated credit bureau data.
The study was based on 152 million transactions by 316,719 small firms that completed loan applications. Around 50% of them were repeat applicants.
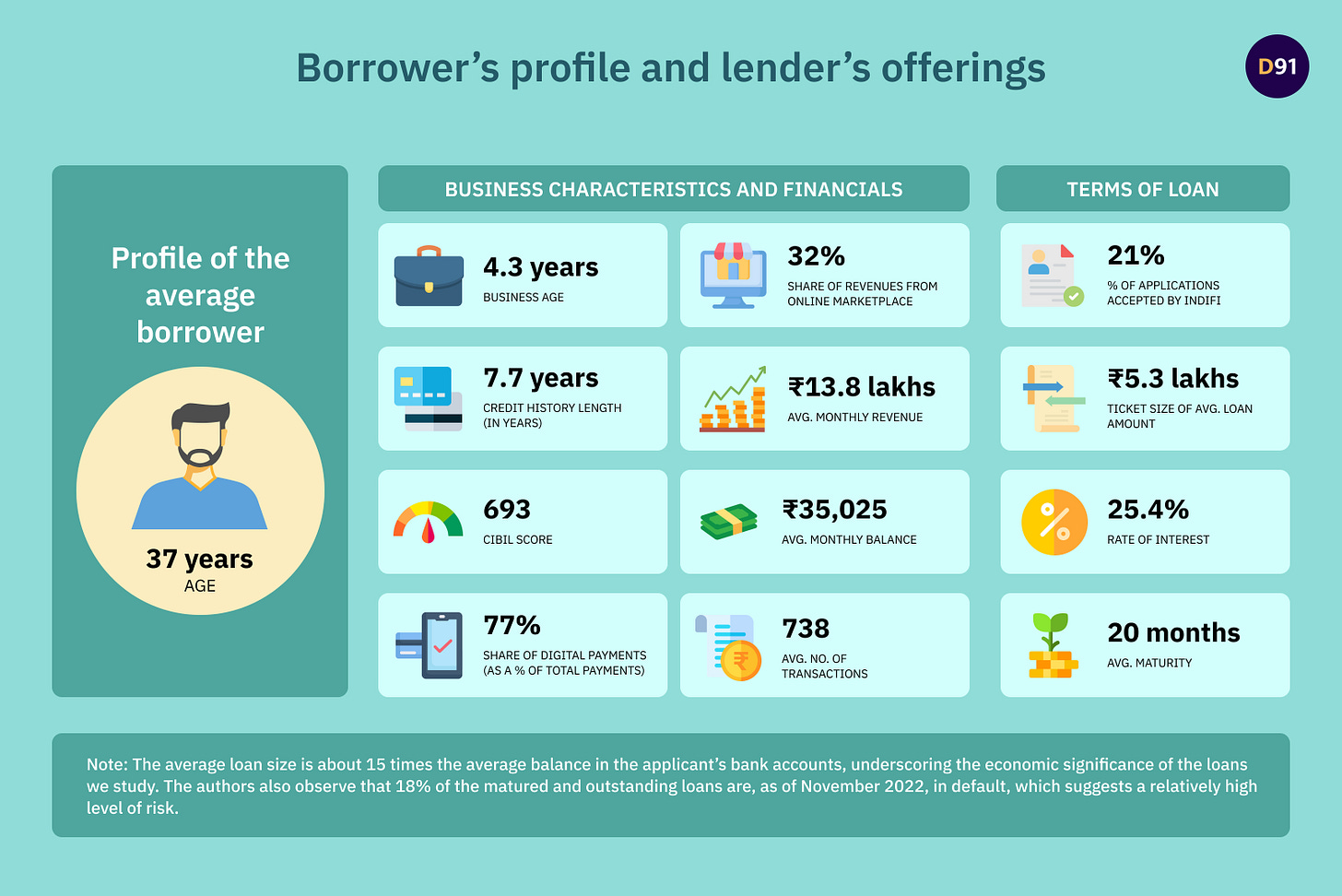
Borrower’s profile and lender’s offerings
The following infographic is a snapshot of typical customer of Indifi and the terms of business related loan offered by the fintech company.
Wondering about the top takeaways for a digital lender? Here are a few -
Increased Likelihood of Loan Approval: Businesses that use cashless payments more frequently are significantly more likely to have their loan applications approved.
Lower Interest Rates and Higher Loan Amounts: On average, businesses with higher cashless payment usage receive lower interest rates and larger loan amounts, even after controlling for other factors like credit score and industry.
Reduced Default Risk: Businesses that rely heavily on cashless payments are less likely to default on their loans. The transparency offered by digital payment records helps lenders assess the risk more accurately, reducing the chances of lending to high-risk borrowers.
The graphs below depict the relationship between the cashless/digital payments and the access to digital credit. For all parameters, it shows a positive relationship.
Fair enough - but why does this happen?
Well firstly, digital payment provides a transparent, trackable record of a business’s financial activities. Fintech lenders use this data to assess business cashflow, spending habits and financial discipline. Secondly, these businesses are also seen to be creditworthy because they are less likely to divert the company’s resources for personal use or to engage in risky financial behaviour. And thirdly, the data shows that digital payments are particularly effective at predicting default risk. In fact, this predictive power is so strong that it outperforms traditional credit scores in some cases, especially when the data includes detailed insights into payment outflows.
Cashless payment usage is of particular interest for lenders because it provides incremental information about downside risk that is not captured by usual observable measures such as credit score, business model, industry, or any fixed characteristic.
The Future of FinTech Lending: Open Banking and Beyond
As cashless/digital payments continue to gain prominence globally, the research suggests that their role in lending decisions will only grow. Platforms that combine payments and lending, such as FinTech and BigTech companies, are uniquely positioned to harness the power of payment data to streamline loan approvals, reduce default risks, and offer more personalized financing solutions.
This shift also underscores the importance of open banking, which allows third-party platforms to access financial data and offer innovative lending solutions. Regulatory efforts to promote open banking are already underway in many jurisdictions, and these efforts could further improve access to credit for businesses and consumers worldwide.
Conclusion
Digital payments are not just changing the way businesses transact; they are transforming the lending landscape, offering small businesses easier access to capital and more favourable loan terms. By providing lenders with a transparent, real-time view of a business's financial behaviour, cashless payment records serve as powerful tools for evaluating creditworthiness, reducing default risk, and promoting financial inclusion. As the use of digital payments continues to rise, we can expect even greater improvements in financial intermediation, making it easier for businesses of all sizes to thrive.
Ghosh, Pulak and Vallee, Boris and Zeng, Yao, FinTech Lending and Cashless Payments (March 9, 2022). Proceedings of Paris December 2021 Finance Meeting EUROFIDAI - ESSEC, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3766250 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3766250
In this study, payments records are categorized into two groups - cash and cashless. payments. Cash payments are cash deposits or withdrawals, either at a branch or an ATM. Cashless payments include any non-cash payments for which they identified the payment technology. Specifically, cashless payment technologies in the data include certified checks, Internet banking transfers, mobile banking transfers, Point-of-Sale (POS) machine transactions, and transfers in third-party mobile applications.
All artworks are designed by Smriti Krishna.
If you enjoyed reading this blog and would like to receive more such articles from D91 Labs, please subscribe to our blogs here.
To read more about our work, visit our website




The companies that will automate personalize lending products faster will be positioning themselves as selling shovel in gold rush.